Squeezing at the Normal-Mode Splitting Frequency of a Nonlinear Coupled Cavity
Jun 17, 2025·
,
,
,
,
,
,
·
0 min read
Jonas Junker
First author
,
Jiayi Qin
Vaishali B. Adya
Nutsinee Kijbunchoo
Sheon S.Y. Chua
Terry G. McRae
Bram J.J. Slagmolen
David E. McClelland
Abstract
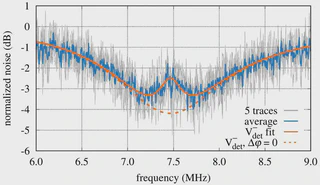
Coupled optical cavities, which support normal modes, play a critical role in optical filtering, sensing, slow-light generation, and quantum state manipulation. Here, we report the first experimental demonstration of squeezing generated in a quantum-enhanced coupled-cavity system, achieving a quantum noise reduction of 3.3 dB around the normal-mode splitting frequency of 7.47 MHz. We provide a comprehensive analysis of the system’s loss mechanisms and performance limitations, validating theoretical predictions and highlighting potential applications in precision sensing and gravitational wave detection. :contentReference[oaicite:1]{index=1}
Type
Publication
Physical Review Letters